Face Liveness Detection
Anti-spoofing Presentation Attack Detection (PAD)
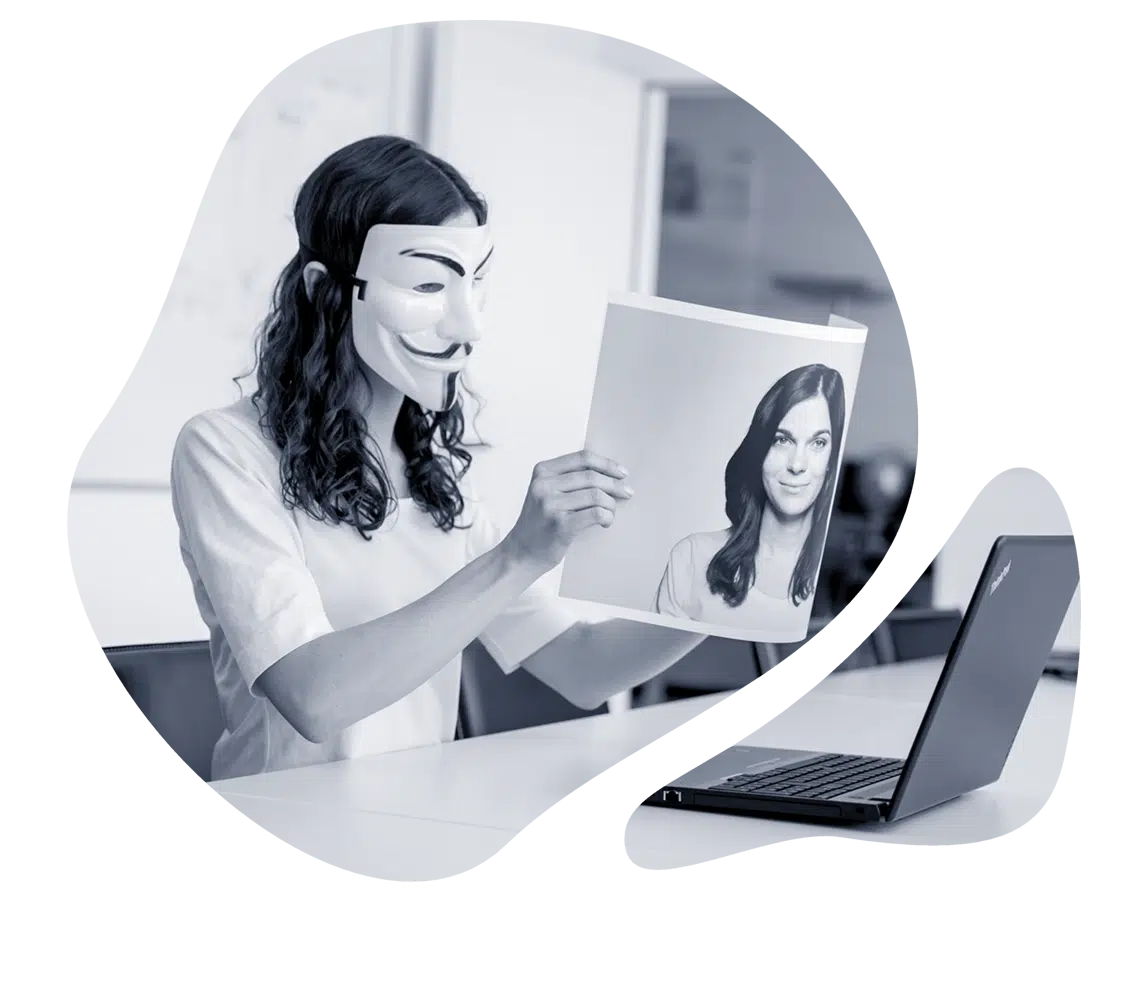

Our liveness detection software prevents spoofing in both presentation attacks and deepfakes. It builds trust in online transactions by ensuring that the person authenticating is real and physically present in front of the camera.

How does Liveness Detection work?
Facial Liveness Detection
A unique fusion technology
1
3D Object Validation
By capturing only two images using any standard camera, BioID’s unique motion-analysis algorithm validates whether the face detected is indeed from a real person.
2
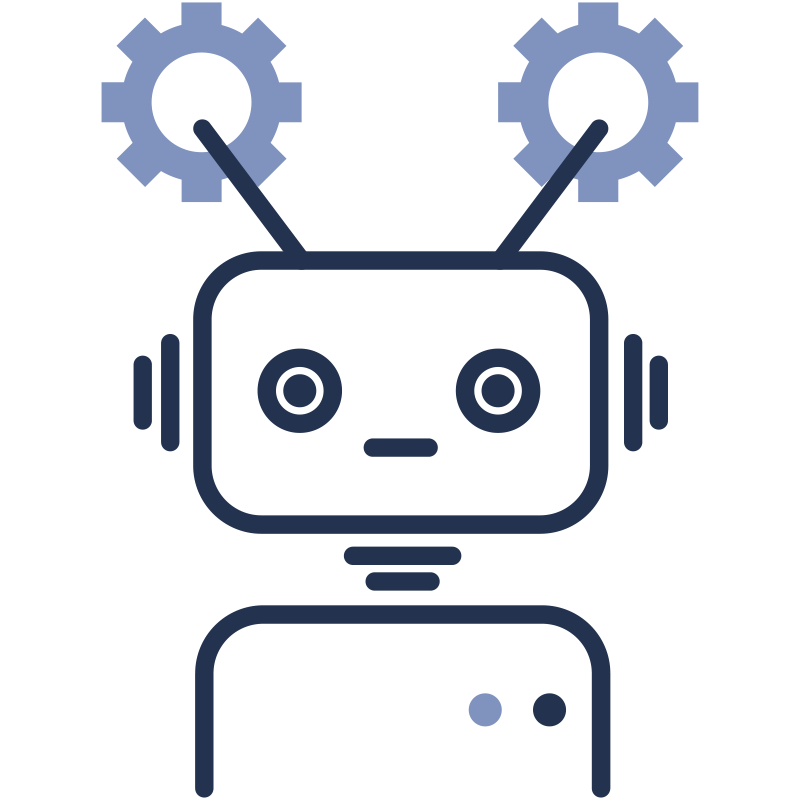
AI Technology
Powerful DNNs (deep neural networks) are used to detect presentation attacks like 3D masks, video replays, projections, etc.
3

Deepfake Check
Sophisticated algorithms are incorporated to reject images/videos that have been manipulated using deepfake tools.
4
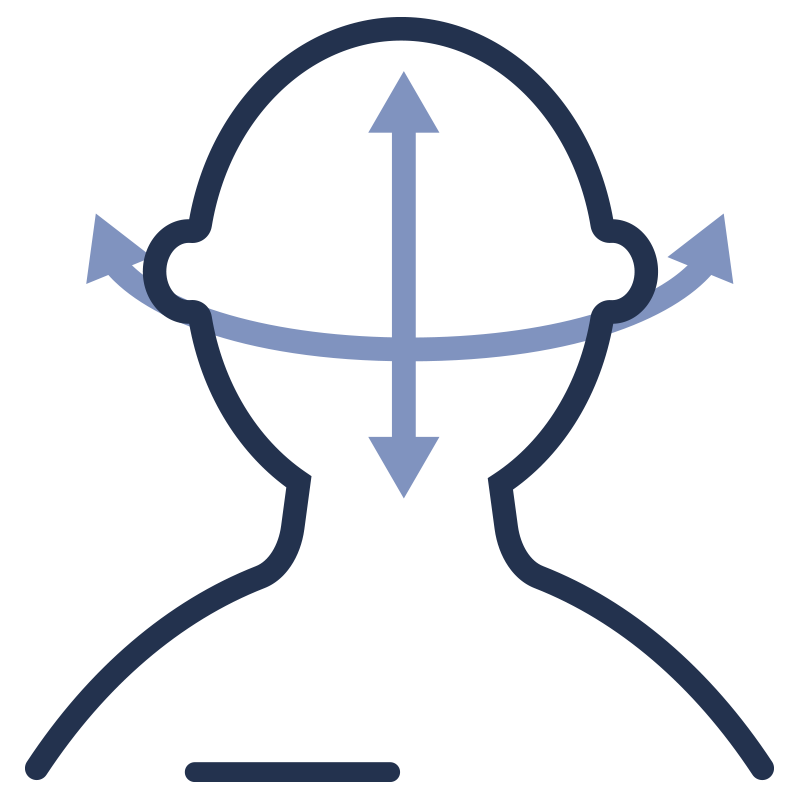
Challenge-Response
Optional patented user interaction to obtain ‘user consent’ during the video liveness check.
Deepfake and Identity Fraud Defense
Deepfakes are fake videos, photos, or audios produced by artificial intelligence. People’s faces, actions, or voices are adjusted in a certain way, meaning they can be shown in literally any situation, saying whatever the deepfake creator wants them to.
The term “deepfake” is a combination of the English words “deep learning” and “fake”. It describes the artificial generation or modification of video and audio content using AI technologies. Deepfakes use artificial neural networks and machine learning methods, especially deep learning.
The tools behind Deepfakes have seen remarkable improvements in usability and quality since their inception. This improvement, combined with the increased digitization driven by the COVID-19 era and the delay in protection legislation, has created a worrisome combination. As technology evolves, finding comprehensive solutions to the deepfake challenge remains essential to protecting digital ecosystems and society.
BioID sees deepfakes, specifically when combined with video injection attacks, as the latest frontier in fraud-fighting. Our engagement in FAKE-ID, a project on deepfake detection funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) highlights this.
Deepfake detection is an integral part of the BioID’s software service, thus securing our customers’ systems from identity fraud.
Try out the demo on BioID’s Playground or the API by requesting a trial instance.
ISO/IEC 30107-3 compliance
Confirmed by TÜViT
BioID’s face liveness verification is compliant with industry standards, as confirmed by two independent FIDO-accredited testing laboratories
- ISO/IEC 30107-3:2017 Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) Levels 1 & 2 compliant as certified by TÜV Informationstechnik GmbH (TÜViT) in Germany.
- FIDO ISO 19795 and ISO/IEC 30107 Biometric Component as certified by laboratories ELITT/Leti in France. BioID’s anti-spoofing technology is a vital part of the standard specifications for fraud prevention, including deepfake detection.
- BioID’s certified liveness detection is compliant with the standard for Remote Identity Verification Providers (PVID) as published by ANSSI (The National Information Systems Security Agency). In 2022, BioID has been tested successfully as part of a PVID certified identity verification solution.
FAQs
What is Liveness Detection?
Typically referred to as Presentation Attack Detection or PAD, it validates whether a user is physically present in front of the camera. It is a crucial component in the fight against deepfakes and fraudulent identity authentication. It distinguishes live persons from spoofing attacks by means of presenting to the camera a photo/video of a person or impersonating a person using a face mask without the physical presence of the impersonated person. It is a software-based technology generally used in conjunction with face recognition.
Why Liveness Detection?
It is needed to secure an online transaction from spoofing attacks, such as deepfakes. For instance, a fraudster could use a photo, video, or mask of a legitimated person to spoof a facial recognition system and gain unauthorized access to accounts or data.
How does it work?
It is designed to effectively detect and prevent presentation attacks, like deepfakes. Image processing algorithms analyze images or videos and decide whether they were captured by a live person. Software-based technologies include motion analysis, texture analysis, artificial intelligence (AI), or a combination of the above. Hardware-based solutions are typically those relying on the use of a 3D camera and/or multiple cameras.
What is a Challenge-Response?
A challenge-response system requires the user to correctly respond to a specific action prompted by the ‘challenge’. A challenge-response system is the most effective means to ensure user consent protecting both system integrity and data privacy. In a typical face application with challenge-response, the user is prompted to turn the head in one or more random directions. Only when the requested head directions were followed by the user correctly, the challenge-response is considered successful. The more challenges used, the higher the level of security, as it is more challenging for an attacker to have a video or deepfake recording showing exactly these head movements.
Active or Passive?
Active liveness detection requires the user to react in a certain way. In particular, it requires a user to intentionally confirm his or her presence by interacting with the system (e.g. by nodding) and is therefore particularly useful for applications requiring user consent putting high importance on data privacy. For fighting attacks at the application level, e.g. through the injection of modified camera streams, challenge-response mechanisms can be utilized to reject prerecorded videos/deepfakes.
Passive liveness detection is a method that does not require any specific actions from the user. Therefore, it is possible to perform passive LD without the user’s interaction, by focusing on usability.
Effective Mechanism against Spoofing Attacks
BioID Web Service (BWS) aims to generate the same trust and user experience as face-to-face interaction. As a result, a series of liveness verification mechanisms for anti-spoofing were developed and introduced as early as 2009. The essence is to make sure submitted recordings were indeed taken from a live person in front of the camera.
The latest mechanism for Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) prevents forgery through replay attacks like videos, recorded deepfakes, or avatars. It is based on texture detection and AI.
By means of texture analysis, the texture of a recaptured image, a video, a projection, or other fake attempts is now detected for reliable biometric anti-spoofing. Today, PAD detects even remote-controlled 3D avatars, deepfakes, as well as 3D masks. BioID has earned another patent for its liveness detection technology.
It is based on an optical flow algorithm to discern between a 2D and a 3D object. By means of a simple but sensitive motion trigger, the algorithm captures images automatically, preventing an attacker from presenting or swapping different photos.
Liveness Verification for Face Recognition
There are various ways to detect presentation attacks in biometrics. Hardware-dependent techniques use 3D cameras to look for depth information from a 3D face or infrared cameras to detect thermal information. However, both require special equipment and are therefore not compatible with most webcams and mobile phone cameras available today. Instead, the BioID liveness detection algorithm works camera-independently.
Besides BioID’s challenge-response patent from 2004, one of the first solutions on the market was eye blinking detection, measuring intrinsic facial movement. This seems reasonable; after all, a photo cannot blink. Or can it? An attacker can simply take a photo, cut out holes for the eyes, hold it in front of their face, and blink. If done carefully, this can fool many blink detection systems. A video of the person blinking would also work.
Additionally, these systems are inconvenient for users as they take a comparably long time for liveness checks. A similar technique prompts the user to smile to verify their presence. Some mechanisms look for pupil dilation, for instance, by making the screen dark and then suddenly bright. This can successfully detect fakes but is also vulnerable to a photo with eye holes or a well-timed video.
Thus, a combination of techniques is ideally the most reasonable approach to coping with different (deepfake) attack scenarios. Today, BioID combines traditional approaches from more than 20 years of experience with the latest AI deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs).
Interested in pricing options for our biometric authentication service BWS?
Made in Germany
since 1998

Originating from the research institute Fraunhofer IIS in 1998, BioID is a German biometrics company.
Our technology has a proven record since its inception and is trusted by countless enterprises, banks, and government organizations.
